Treatments for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
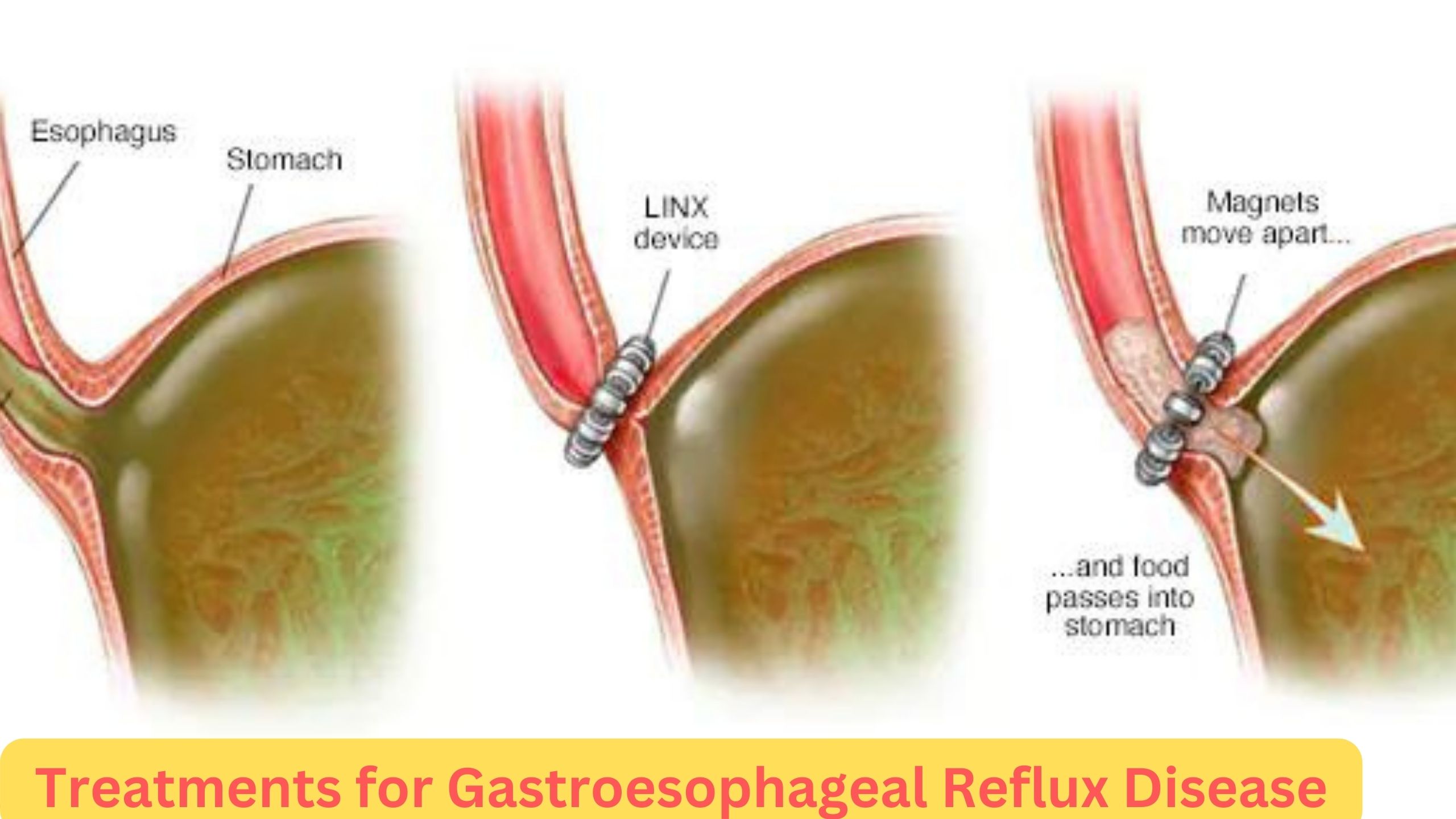
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, leading to irritation. Effective management of GERD involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions. Understanding these treatment options can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from this condition.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage GERD
Weight Management
Losing weight is one of the most effective lifestyle changes for managing GERD. Excess weight can put pressure on the abdomen, pushing stomach contents up into the esophagus. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce this pressure and minimize reflux symptoms.
Sleeping Position
Elevating the head during sleep can prevent nighttime symptoms. Using a foam wedge or extra pillows to incline your body can help keep stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. The head should be raised 6 to 8 inches for optimal results.
Quit Smoking
Quitting smoking is crucial for GERD management. Smoking weakens the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), making it easier for stomach acid to backflow into the esophagus. By stopping smoking, you can strengthen the LES and reduce reflux episodes.
Dietary Adjustments
Changing your eating habits and diet can also alleviate GERD symptoms. Eating smaller, more frequent meals instead of large meals can prevent the stomach from becoming too full. Avoiding foods and drinks that trigger reflux, such as fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and chocolate, is also beneficial.
Medications for GERD
Over-the-counter and prescription medications play a significant role in managing GERD. If lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following medications:
Antacids
Antacids can provide quick relief for mild heartburn by neutralizing stomach acid. They are available over the counter, but should not be used daily or for severe symptoms without consulting a doctor, as they can cause side effects like diarrhea or constipation.
H2 Blockers
H2 blockers reduce the amount of acid the stomach produces. They are effective for healing the esophagus and are available both over the counter and by prescription. However, they are generally less effective than proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are more effective than H2 blockers for treating GERD. They reduce stomach acid production significantly and help heal the esophageal lining in most patients. PPIs are available over the counter and by prescription and are safe for long-term use under medical supervision. Side effects are rare but can include headache, diarrhea, and upset stomach. There is ongoing research into the long-term effects of PPI use.
Other Medications
If antacids, H2 blockers, and PPIs are not effective, doctors may prescribe other medications to manage GERD symptoms. These could include prokinetics, which help empty the stomach faster, or medications that strengthen the LES.
Surgical and Medical Procedures
Surgery may be recommended for severe GERD cases or when long-term medication use is undesirable. Surgical options include:
Fundoplication
Fundoplication is the most common surgical procedure for GERD. During this operation, a surgeon wraps the top of the stomach around the end of the esophagus to strengthen the LES and prevent reflux. This procedure can be performed laparoscopically, which involves small incisions and leads to shorter recovery times, or through open surgery, which requires a larger incision.
Weight-Loss Surgery
For individuals with obesity, weight-loss surgery (bariatric surgery) can help reduce GERD symptoms. Gastric bypass surgery is particularly effective, as it helps patients lose weight and reduces the likelihood of acid reflux.
Endoscopic Procedures
In certain cases, endoscopic procedures can be used to treat GERD. These minimally invasive techniques involve using an endoscope to either reinforce the LES or deliver radiofrequency energy to the esophageal sphincter. However, these procedures are not as common as fundoplication.
Conclusion
Effective management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and possibly surgical interventions. By understanding and implementing these treatments, individuals can significantly reduce their symptoms and improve their quality of life.